强网杯S9 2025 初赛 - bph
文件属性
| 属性 | 值 |
|---|---|
| Arch | amd64 |
| RELRO | Full |
| Canary | on |
| NX | on |
| PIE | on |
| strip | yes |
| libc | 2.39-0ubuntu8.6 |
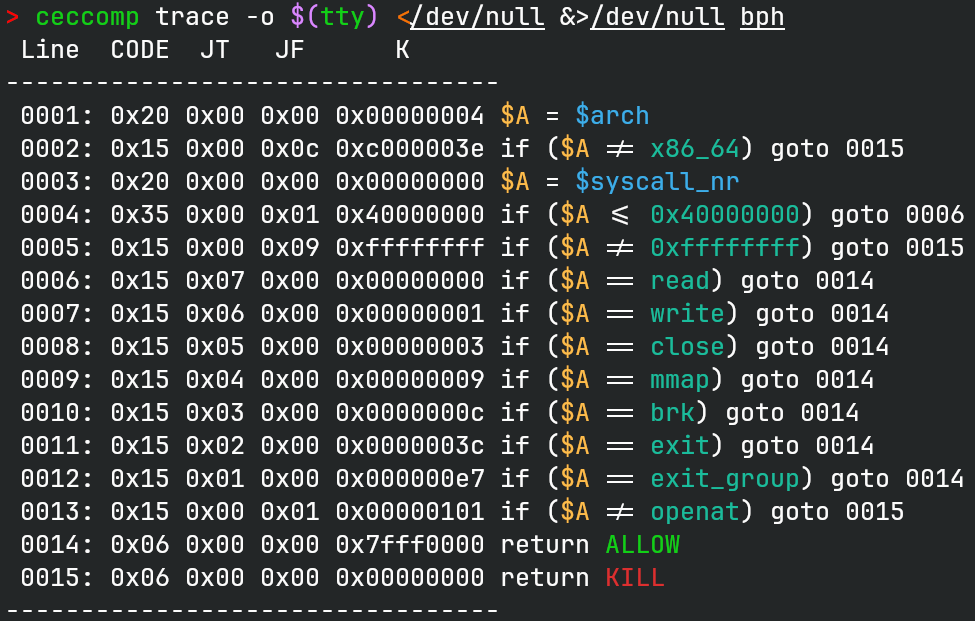
seccomp rules
解题思路
寻找漏洞
题目附件只给了ELF,也不给一下libc...看星盟的wp说是Ubuntu 24.04
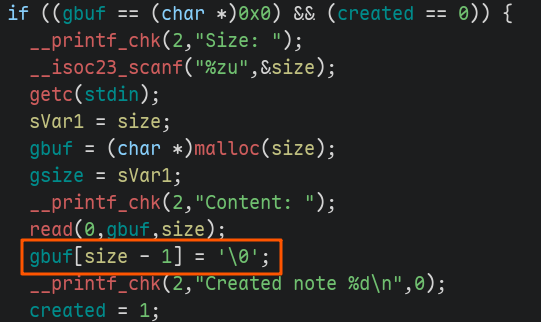
题目中就两个漏洞:部分写入导致的信息泄露,以及在执行create时对malloc结果不做检查,
直接写'\0'导致的任意地址写0。
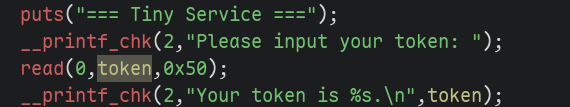
检查我们首次输入内容时可以泄露的内容,有堆、栈、程序基址、libc和libseccomp,
然而只能取其一,那我们选择泄露free的地址来获取libc基址。
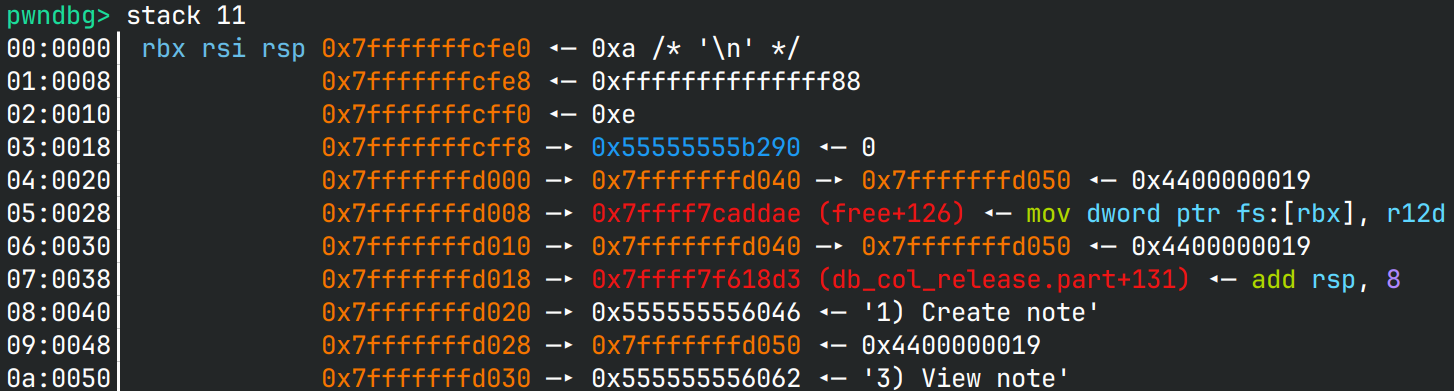
任意写0到任意写
接下来怎么利用这一个0字节来利用呢?首先我们需要更多输入,那么阅读fgets的源码,
一步一步向里跟踪,可以找到这么一条要求用户输入的链子:
_IO_fgets -> _IO_getline -> _IO_getline_info -> __uflow --> _IO_UFLOW
查找跳表,是执行_IO_default_flow,接着执行_IO_UNDERFLOW,展开为_IO_new_file_underflow,
最后调用read从标准输入中读取更多内容。
1 | int |
只要我们控制了stdin->_IO_buf_base,由于原来stdin->_IO_buf_end指向其_shortbuf + 1,
我们就可以向其中填充大量数据。想要触发read读取数据,需要满足read_ptr >= read_end,
否则会走解析已有数据的路径:
1 | size_t |
换句话说,每次都会先消耗完所有的缓冲区字节后,才会走触发read的分支。
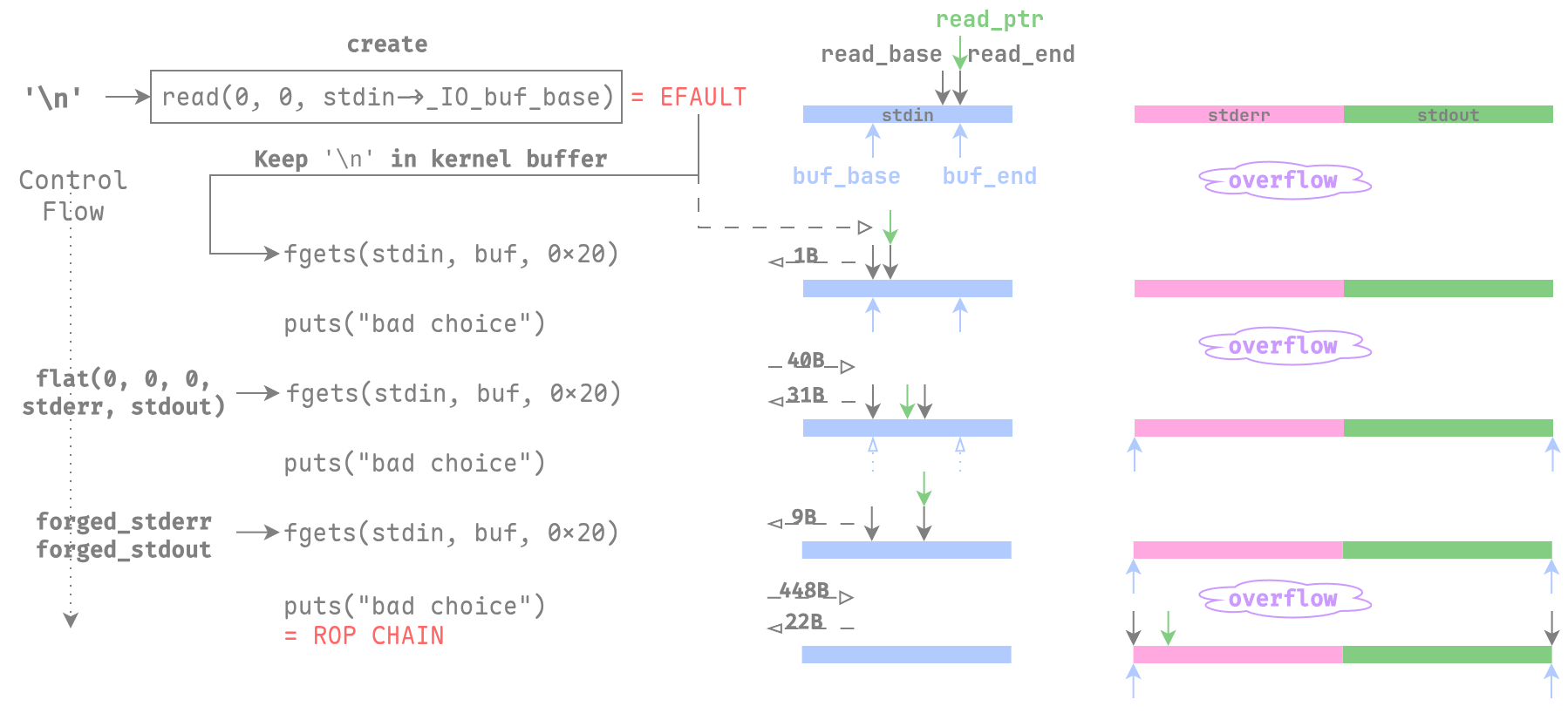
现在我们考虑如何输入能保证让glibc去读取我们想要的输入呢?首先create时,
read(0, 0, size)也会触发阻塞,但是我们输入任何东西都会使read返回EFAULT,
并使其滞留在缓冲区中。像我这样,输入一个'\n',会让fgets获取之,
然后read_ptr = buf_base, read_end = buf_base + 1,接着fgets返回,
显示"bad choice"。接下去回到fgets,先前消耗掉的'\n'使得缓冲区耗尽
(read_ptr += 1, read_ptr == read_end),所以又需要刷新缓冲区。
此时我们将buf_base和buf_end写为_IO_2_1_stderr_和stdout,
然后fgets没有遇到换行符,消耗0x1f字节,缓冲区剩余40 - 0x1f = 9 < 0x1f。
这里注意不能多发送一个换行符,不能用t.sendline,因为_IO_buf_end后面邻接的是_IO_save_base,
在__uflow过程中会free之,多一个换行符使其变为0xa,会导致 SEGV。
这样返回一个"bad choice"后,再次进入fgets获取0x1f字节,发现缓冲区耗尽,
又一次刷新缓冲区,此时我们就能往_IO_2_1_stderr_和_IO_2_1_stdout_中写入数据了。
我们往_IO_2_1_stderr_中写入ROP链(反正用不到),再往_IO_2_1_stdout_伪造结构体,
就可以套House of Apple 2的链子去劫持控制流。可以参考下图作为读入字节流的情况。

任意写到栈迁移
在能控制_IO_2_1_stdout_后,我们就可以打House of Apple 2来劫持程序控制流。
但是题目有沙箱,必须要走ROP链才有机会能执行orw打印flag。首先要找一个合适的gadget来做栈迁移,
过往的setcontext gadget感觉如今用起来有些限制,所以我决定爆搜libc,看看有没有别的gadget。
写了一个调用capstone的脚本来找,看起来gadget很多,但其实能用的不多。
1 | #!/usr/bin/python |
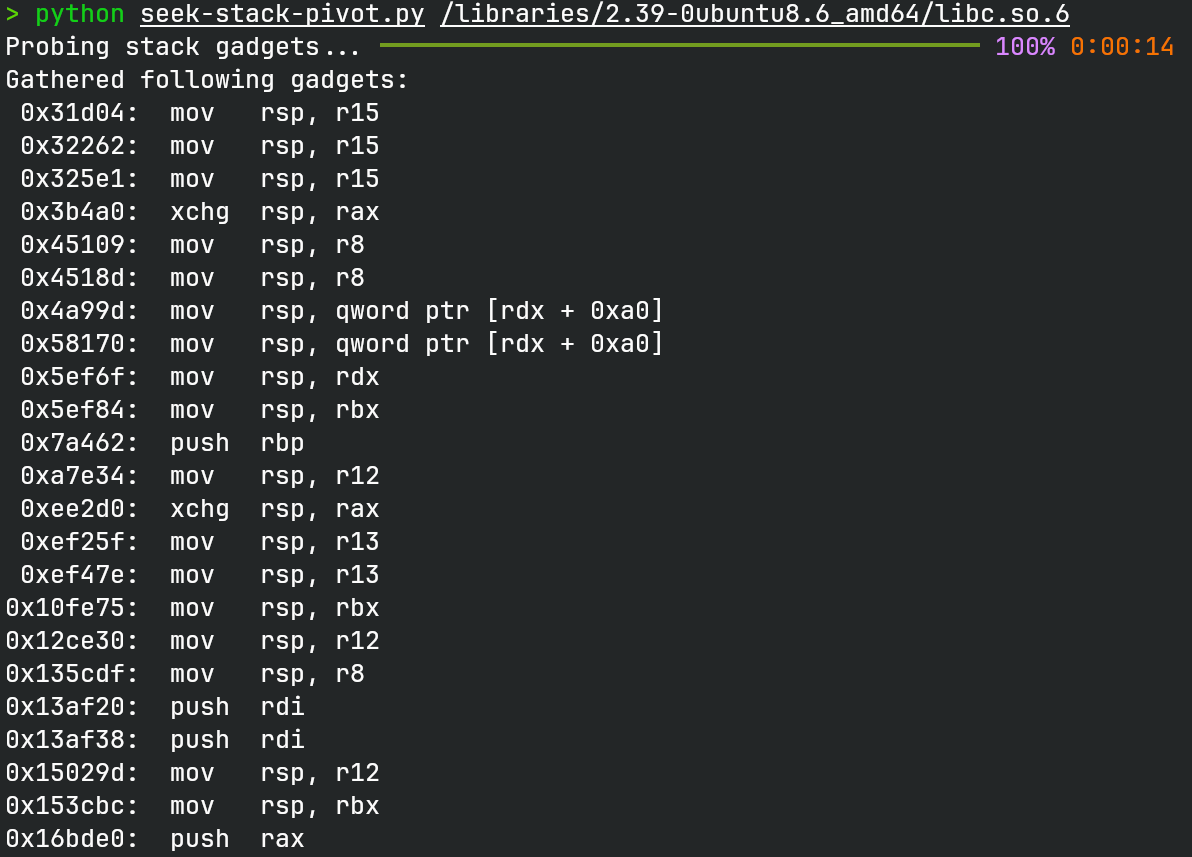
其中最好用的是0x5ef6f这个,对应__push___start_context+63,即mov rsp, rdx; ret;,
只要能控制rdx就可以。这个gadget你甚至直接能用ropper搜出来,比setcontext还好用。
最后我们的目标就是控制rdx,这样我们就能控制栈了。
House of Apple 2 实现栈迁移
有没有什么办法,能在执行House of Apple 2攻击时,顺便把rdx也给控制了呢?
看一下这个版本函数的汇编的结果,在写入read_stop时,将_IO_read_ptr加载到了rdx中。
而在_IO_wdoallocbuf函数中没有变更rdx的值,因此我们只要能控制_IO_read_ptr,
就能控制rdx,显然可以做到。
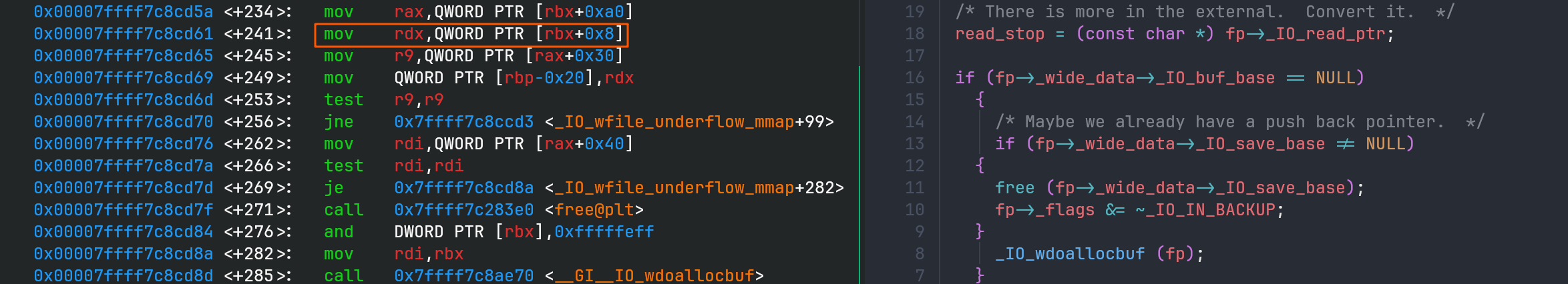
最后整理一下:在_IO_2_1_stderr_写rop链,在_IO_2_1_stdout_劫持程序流到栈迁移gadget,
并且准备_IO_read_ptr来控制rdx为_IO_2_1_stderr_,就可以在puts时触发rop链打印flag。
到这里为止,就能顺利构造exp了。相比星盟的方案,避免了控制rcx的问题,更加直接了些。
不受干扰的栈迁移gadget
__push___start_context处的gadget简单好用,它会不会受编译器影响呢?寻找这个函数,发现其位于
glibc/sysdeps/unix/sysv/linux/x86_64/__start_context.S,是手写汇编,因此,一直存在。
那么它是什么时候出现的呢?使用git blame,找到这一段的编辑是在7年前的这个commit引入的,
对应到版本是> glibc-2.27,也就是说从18年到现在都存在这个问题。
可以说是现在越来越安全的情况下的通解之一了。
最讽刺的是这个函数明明是为了引入shadow stack这么一个安全特性而引入的, 却为ROP攻击留下了巨大的隐患。补上了一个洞,却又打开了另一扇门。
EXPLOIT
1 | from pwn import * |
参考
- 标题: 强网杯S9 2025 初赛 - bph
- 作者: RocketDev
- 创建于 : 2025-10-26 00:50:00
- 更新于 : 2025-10-26 01:01:00
- 链接: https://rocketma.dev/2025/10/25/bph/
- 版权声明: 本文章采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 进行许可。